Senior Network Engineer focused on networking, security, and automation.
[My journey to CCIE Automation #7] Exploring Model-Driven Telemetry for real-time network insights
In blog #7 of the CCIE Automation journey, Model-Driven Telemetry is explored to collect real-time data from network devices. Using Ansible, Telegraf, InfluxDB, and Grafana, a solution is built to stream, store, and visualize telemetry metrics for improved network insight.
![<span id="hs_cos_wrapper_name" class="hs_cos_wrapper hs_cos_wrapper_meta_field hs_cos_wrapper_type_text" style="" data-hs-cos-general-type="meta_field" data-hs-cos-type="text" >[My journey to CCIE Automation #7] Exploring Model-Driven Telemetry for real-time network insights</span>](https://sicra.no/hs-fs/hubfs/two_guys_working_on_a_computer.jpg?width=1024&height=576&name=two_guys_working_on_a_computer.jpg)
(This article was originally published on Bluetree.no. Following the merger of Sicra and Bluetree, content from Bluetree has now been migrated to Sicra.)
[My journey to CCIE Automation #7] Exploring Model-Driven Telemetry for real-time network insights is part of an ongoing CCIE Automation series. In the previous blog, I worked with infrastructure as code and Cisco ACI. This time, I explore Model-Driven Telemetry to stream real-time data and gain better insight into network state.
Blog #7
This time I wanted to dive deeper into Model-Driven Telemetry (MDT). Instead of manually polling devices for operational data, MDT allows streaming real-time metrics from network devices to monitoring systems — giving insights into performance, state, and anomalies as they happen.
Why Model-Driven Telemetry?
Model-Driven Telemetry is the foundation for proactive, data-driven network operations. It lets us:
-
Stream metrics from devices in real-time (CPU, memory, interfaces, BGP peers)
-
Use YANG models to define exactly what data we want
-
Choose between periodic polling, periodic push, or event-driven subscriptions
-
Visualize data in Grafana or feed it into analytics platforms
This time's project
I created a MDT solution for Cisco IOS-XE devices, integrated into my Nautix platform:
-
Subscriptions: Created using YANG models to collect CPU, memory, temperature and CDP neighbors operational data
-
Streaming: Configured dial-out gRPC telemetry to Telegraf
-
Visualization: Built Grafana dashboard showing device metrics
-
Optimization: Tuned subscriptions with XPath filters, cadence settings, and on-change triggers
Getting started
Before configuring telemetry on your devices, you need the TIG stack (Telegraf → InfluxDB → Grafana) to receive and visualize the data. Here’s how I set it up locally using Docker Compose.
1. Start the TIG stack
I assume you have already cloned the repository and have done the initial setup as per readme.
In the root of the repositoryrepo, do:
-
docker-compose up
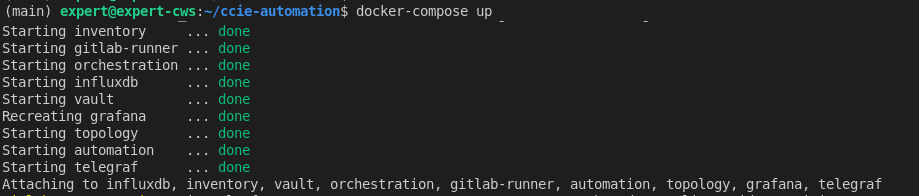
This spins up:
-
InfluxDB – stores telemetry data
-
Grafana – dashboards and visualization
-
Telegraf – optional local agent if needed for transformation or collection
-
Other Nautix services
2. Run the Ansible playbook
Configure telemetry subscriptions on your devices (ensure you have run device discovery first):
-
docker exec -it automation ansible-playbook -i ansible/hosts.yml ansible/configure_telemetry.yml
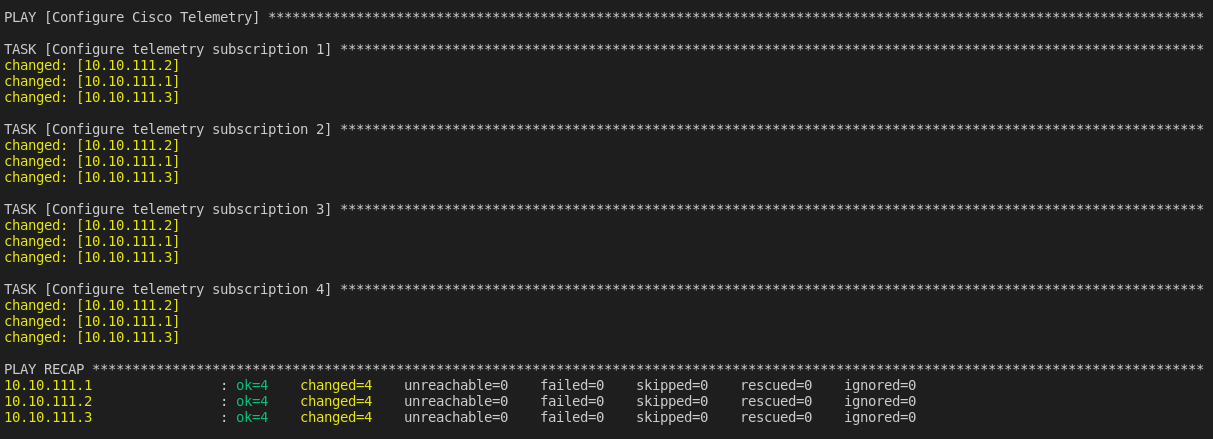
This playbook:
-
Creates subscriptions using YANG models
-
Configures cadence, on-change triggers, and dial-out streams
-
Points the telemetry data to your InfluxDB instance
3. Check the telemetry stream
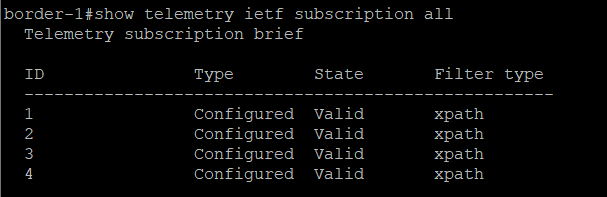
On the devices, verify subscriptions:
-
show telemetry ietf subscription all
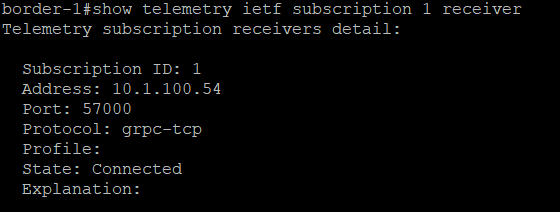
Check that the subscription is connected to Telegraf:
-
show telemetry ietf subscription 1 receiver
4. Visualize in Grafana
-
-
Open Grafana (http://localhost:3000), login with admin/secret
-
Add an InfluxDB data source pointing to your InfluxDB container
-
Import dashboard: services/grafana/nautix_dashboard.json
-
Explore real-time device metrics in the dashboard
-
Implementation
Here’s the updated folder structure reflecting new or modified files:
File: services/automation/ansible/
-
configure_telemetry.yml – Ansible playbook to create telemetry subscriptions (new/updated)
-
group_vars/discovered.yml – Variables used for telemetry configuration
File: services/grafana/
-
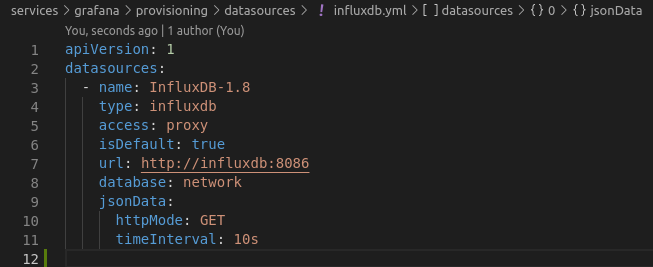
influxdb.yml – Grafana data source configuration for InfluxDB
-
nautix_dashboard.json – Exported dashboard
File: services/telegraf/
-
telegraf.conf – Telegraf configuration
File: docker-compose.yml – Spins up InfluxDB, Grafana, Telegraf, and rest of the Nautix app
Let's break it down step by step
1. Ansible playbooks
-
configure_telemetry.yml sets up telemetry subscriptions on Cisco IOS-XE devices using YANG xpath
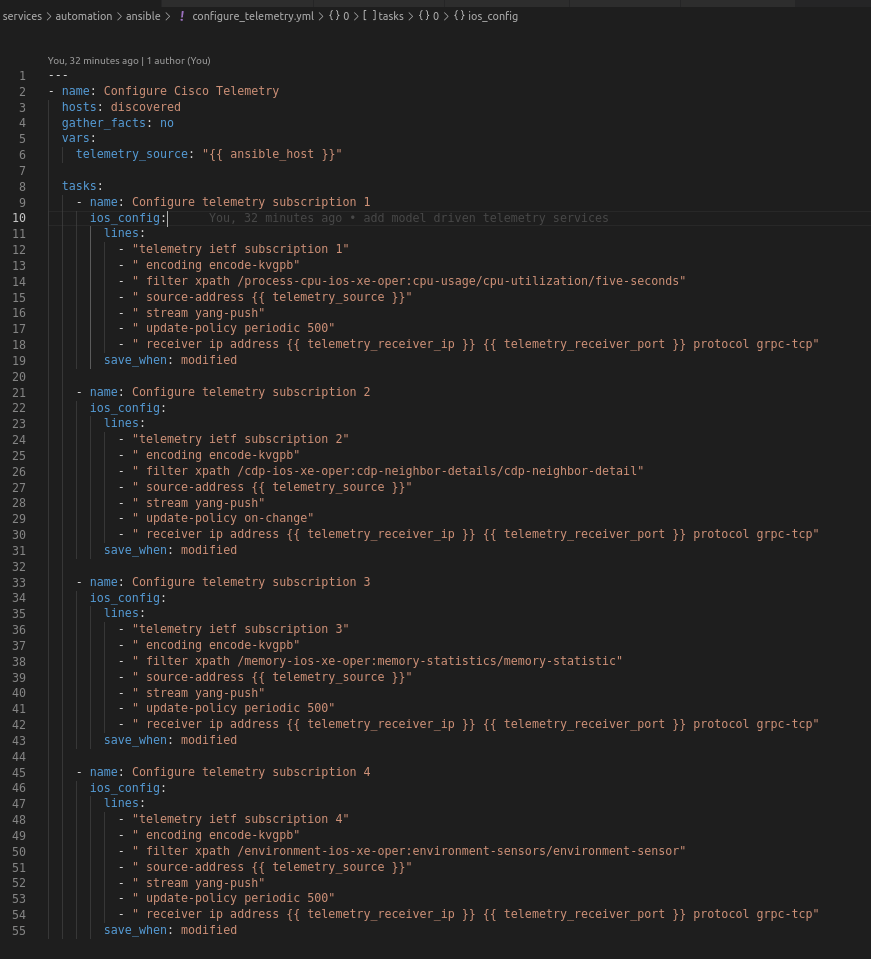
-
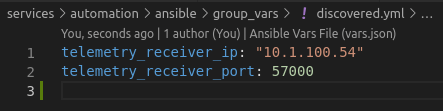
Variables in group_vars/discovered.yml are used for dynamic configuration
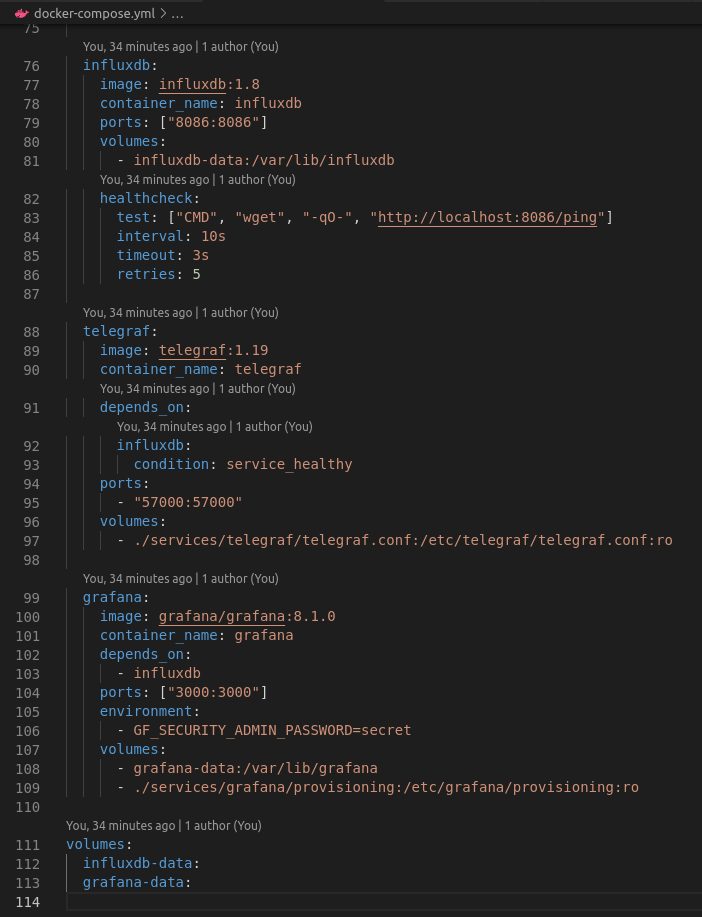
2. TIG stack
-
Docker Compose starts Telegraf, InfluxDB and Grafana, providing a fully integrated telemetry environment
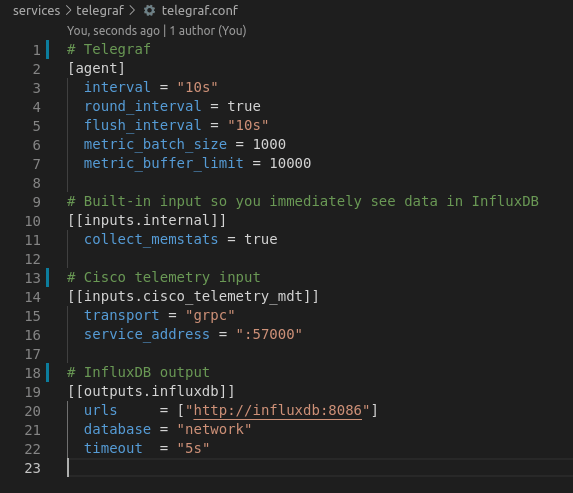
3. Telegraf configuration
-
Configured via telegraf.conf to parse telemetry streams from devices and forward metrics to InfluxDB
4. Influx DB configuration
-
Set up very basic
Why this matters
Before, operational data required manual CLI commands or SNMP polling.
Now:
-
Metrics are streamed continuously, reducing lag
-
On-change subscriptions minimize unnecessary data
-
Dashboards provide actionable insights at a glance
Nautix architecture
Use case "I": Model driven telemetry
-
I.1 Trigger ansible playbook to configure telemetry subscription on Cisco IOS XE devices
-
I.2 Ansible runs playbook
-
I.3 Network devices starts sending telemetry data to Telegraf
-
I.4 Telegraf stores the telemetry data to InfluxDB
-
I.5 User shows dashboard
-
I.6 Grafana polls telemetry data from InfluxDB
-
User seeing the telemetry data
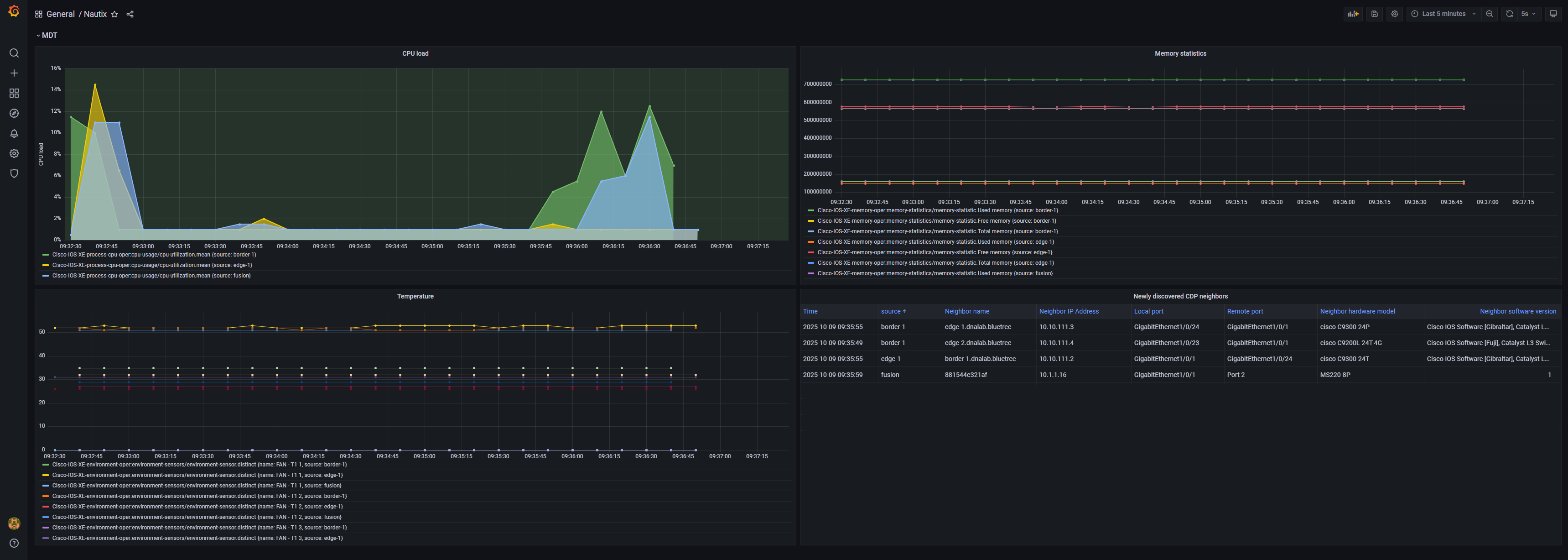
What it looks like in Grafana
What's next
Useful links
- GitLab Repo – My CCIE Automation Code
- Model Driven Telemetry WhitePaper by Cisco
- Ansible documentation
Blog series
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #1] Intro + building a Python CLI app
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #2] Inventory REST API and microservices architecture
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #3] Orchestration API and NETCONF
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #4] Automating network discovery and reports with Python and Ansible
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #8] Exploring ThousandEyes and automating Enterprise Agent deployment
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #9] Applying OWASP Secure Coding Practices
-
[My journey to CCIE Automation #10] From Docker Compose to Kubernetes
Explore more

Cyber Threat Landscape 2026: Insights from Arctic Wolf’s threat report

IAM for dummies
Cost reduction in Microsoft Sentinel and Defender XDR

